Most Viewed Articles
- Blogs >
Fake Currency Detection with Machine Learning
Fake Currency Detection with Machine Learning ¶
Fake Currency Detection is a real problem for both individuals and businesses. Counterfeiters are constantly finding new methods and techniques to produce counterfeit banknotes, which are essentially indistinguishable from real money. At least for the human eye. In this article, I will introduce you to Fake Currency Detection with Machine Learning.
Fake Currency Detection is a task of binary classification in Machine Learning.
Now let’s get started with this task of Fake Currency Detection with Machine Learning. I will start this task by importing the necessary packages:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
The dataset contains these four input characteristics:
The variance of the image transformed into wavelets The asymmetry of the image transformed into wavelets Kurtosis of the image transformed into wavelets Image entropy
The target value is simply 0 for real banknotes and 1 for fake banknotes. Let's read the dataset:
data = pd.read_csv('data_banknote_authentication.txt', header=None) data.columns = ['var', 'skew', 'curt', 'entr', 'auth'] print(data.head())
var skew curt entr auth 0 3.62160 8.6661 -2.8073 -0.44699 0 1 4.54590 8.1674 -2.4586 -1.46210 0 2 3.86600 -2.6383 1.9242 0.10645 0 3 3.45660 9.5228 -4.0112 -3.59440 0 4 0.32924 -4.4552 4.5718 -0.98880 0
Data Exploration : ¶
Now let’s start exploring the dataset. First, I’ll check the data types and if there are any missing values in the data:
print(data.info)
<bound method DataFrame.info of var skew curt entr auth 0 3.62160 8.66610 -2.8073 -0.44699 0 1 4.54590 8.16740 -2.4586 -1.46210 0 2 3.86600 -2.63830 1.9242 0.10645 0 3 3.45660 9.52280 -4.0112 -3.59440 0 4 0.32924 -4.45520 4.5718 -0.98880 0 ... ... ... ... ... ... 1367 0.40614 1.34920 -1.4501 -0.55949 1 1368 -1.38870 -4.87730 6.4774 0.34179 1 1369 -3.75030 -13.45860 17.5932 -2.77710 1 1370 -3.56370 -8.38270 12.3930 -1.28230 1 1371 -2.54190 -0.65804 2.6842 1.19520 1 [1372 rows x 5 columns]>
We, therefore, have no missing values in the data. We can now draw a pair diagram to get an overview of the relationship between all the entities. I will also colour the observations: blue for genuine banknotes and orange for counterfeit banknotes:
sns.pairplot(data, hue='auth') plt.show()
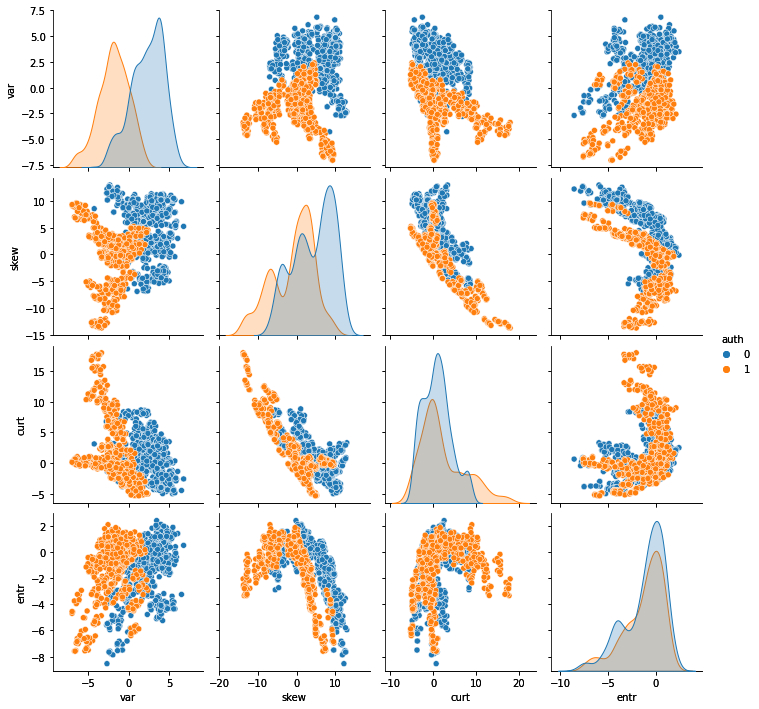
From this pair plot we can make several interesting observations:
- Distribution of both variance and skewness appears to be quite different
- There are clear linear and nonlinear trends in the input features.
- Some characteristics seem to be correlated.
- Some features seem to separate genuine and fake banknotes quite well
Now let’s check if our data is balanced against the target values:
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) plt.title('Distribution of Target', size=18) sns.countplot(x=data['auth']) target_count = data.auth.value_counts() plt.annotate(s=target_count[0], xy=(-0.04,10+target_count[0]), size=14) plt.annotate(s=target_count[1], xy=(0.96,10+target_count[1]), size=14) plt.ylim(0,900) plt.show()
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:5: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The 's' parameter of annotate() has been renamed 'text' since Matplotlib 3.3; support for the old name will be dropped two minor releases later. """ /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:6: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The 's' parameter of annotate() has been renamed 'text' since Matplotlib 3.3; support for the old name will be dropped two minor releases later.

The dataset is fairly balanced, but for the binary classification task, we need to balance it perfectly. So let’s start preprocessing the data by doing just that.
Data Preprocessing : ¶
nb_to_delete = target_count[0] - target_count[1] data = data.sample(frac=1, random_state=42).sort_values(by='auth') data = data[nb_to_delete:] print(data['auth'].value_counts())
1 610 0 610 Name: auth, dtype: int64
Now we have a perfectly balanced dataset. Next, we need to divide the data into training and test sets:
x = data.loc[:, data.columns != 'auth'] y = data.loc[:, data.columns == 'auth'] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
Now I will standardize the data by using the StandardScalar method provided by Scikit-learn:
scalar = StandardScaler() scalar.fit(x_train) x_train = scalar.transform(x_train) x_test = scalar.transform(x_test)
Logistic Regression for Fake Currency Detection ¶
Now, I will train and test our model for fake currency detection by using the Logistic Regressing Algorithm. Let’s first fit the data on the Logistic Regression model to train the model:
clf = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', random_state=42, multi_class='auto') clf.fit(x_train, y_train.values.ravel())
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
Now let’s test the accuracy of our model:
y_pred = np.array(clf.predict(x_test)) conf_mat = pd.DataFrame(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred), columns=["Pred.Negative", "Pred.Positive"], index=['Act.Negative', "Act.Positive"]) tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred).ravel() accuracy = round((tn+tp)/(tn+fp+fn+tp), 4) print(conf_mat) print(f'\n Accuracy = {round(100*accuracy, 2)}%')
Pred.Negative Pred.Positive Act.Negative 187 6 Act.Positive 0 173 Accuracy = 98.36%
Now let’s simulate the prediction of a single banknote.
new_banknote = np.array([4.5, -8.1, 2.4, 1.4], ndmin=2) new_banknote = scalar.transform(new_banknote) print(f'Prediction: Class{clf.predict(new_banknote)[0]}') print(f'Probability [0/1]: {clf.predict_proba(new_banknote)[0]}')
Prediction: Class0 Probability [0/1]: [0.61112576 0.38887424]
Our model predicts that this banknote is real.
Popular Searches
- Thesis Services
- Thesis Writers Near me
- Ph.D Thesis Help
- M.Tech Thesis Help
- Thesis Assistance Online
- Thesis Help Chandigarh
- Thesis Writing Services
- Thesis Service Online
- Thesis Topics in Computer Science
- Online Thesis Writing Services
- Ph.D Research Topics in AI
- Thesis Guidance and Counselling
- Research Paper Writing Services
- Thesis Topics in Computer Science
- Brain Tumor Detection
- Brain Tumor Detection in Matlab
- Markov Chain
- Object Detection
- Employee Attrition Prediction
- Handwritten Character Recognition
- Gradient Descent with Nesterov Momentum
- Gender Age Detection with OpenCV
- Realtime Eye Blink Detection
- Pencil Sketch of a Photo
- Realtime Facial Expression Recognition
- Time Series Forecasting
- Face Comparison
- Credit Card Fraud Detection
- House Price Prediction
- House Budget Prediction
- Stock Prediction
- Email Spam Detection








